Hormone Replacement Therapy
- Energy Boost for Enhanced Workouts
- Natural Thermogenic Properties
- Metabolism Optimization
- Mood and Focus Enhancement

Boost Energy, Mood, and Focus
Hormone Replacement Therapy: Understanding the Basics and Benefits
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) is a medical treatment that involves using hormones to supplement or replace the hormones your body is no longer producing adequately. Typically, HRT is used to manage the symptoms of menopause, but it can also be prescribed for other conditions that involve hormonal imbalances. It is a popular treatment option for patients with hormonal imbalances, menopause symptoms, and gender dysphoria. Hormone therapy may involve using natural or synthetic hormones administered through pills, patches, injections, or topical creams.
Let’s explore the basics of HRT, its benefits, the clinical uses of hormone therapy, the different types of hormone replacement, and the risks associated with this treatment.
Clinical Uses of Hormone Therapy:
Hormone therapy is widely used to treat various health conditions, including menopause symptoms, osteoporosis, and gender dysphoria. Menopause is a natural biological process that occurs in women around 50, where the body gradually stops producing estrogen and progesterone hormones. This can cause symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and mood changes. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) involves using estrogen and progesterone to alleviate these symptoms. HRT can be administered in different ways, including oral pills, transdermal patches, and topical creams.
In addition to managing menopause symptoms, hormone therapy is used to treat osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones. Estrogen therapy can help slow down bone loss and reduce the risk of fractures in postmenopausal women.
Types of Hormone Replacement Therapy
There are two main types of hormone replacement therapy: estrogen-only HRT and combined HRT. Combination therapy involves the use of both estrogen and progesterone and is recommended for women who still have their uterus. Combination therapy is believed to reduce the risk of endometrial cancer, which affects the lining of the uterus.
Estrogen-only HRT is used for women who have undergone a hysterectomy (surgical removal of the uterus) and don’t need to take progesterone to protect against uterine cancer.
Another form of hormone replacement therapy is testosterone replacement therapy, which treats men with low testosterone levels. Testosterone replacement therapy is commonly used to treat symptoms of hypogonadism, a condition in which the testicles do not produce enough testosterone.
Estrogen and Hormone Replacement Therapy: Benefits and Risks for Women
Estrogen is a female hormone that plays a critical role in the reproductive system, 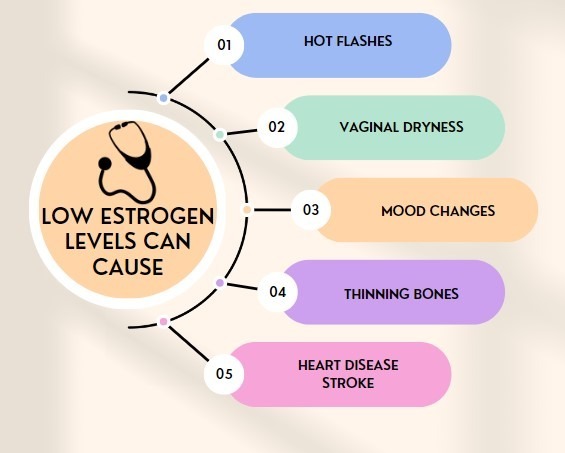 bone health, and cardiovascular health. Estrogen levels decline during menopause, which can cause several symptoms, such as hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and mood changes. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) involves the use of estrogen and/or progesterone to alleviate these symptoms. However, estrogen therapy has been linked to an increased risk of certain cancers, particularly breast and ovarian cancer. This section will explore the benefits and risks of estrogen therapy for women.
bone health, and cardiovascular health. Estrogen levels decline during menopause, which can cause several symptoms, such as hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and mood changes. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) involves the use of estrogen and/or progesterone to alleviate these symptoms. However, estrogen therapy has been linked to an increased risk of certain cancers, particularly breast and ovarian cancer. This section will explore the benefits and risks of estrogen therapy for women.
Benefits of Estrogen Therapy: Estrogen therapy can alleviate the symptoms of menopause and improve bone health in postmenopausal women. Estrogen therapy can also improve cardiovascular health by reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke. Estrogen therapy can also be used to treat other conditions such as breast cancer, where the drug is used to block the production of estrogen, which fuels the growth of cancer cells.
In addition to managing menopause symptoms, estrogen therapy can be used as hormone replacement therapy for transgender women. Estrogen therapy can help suppress the production of endogenous hormones and replace them with hormones that are more aligned with the individual’s gender identity.
Risks of Estrogen Therapy: Estrogen therapy has been linked to an increased risk of certain cancers, particularly breast and ovarian cancer. The Women’s Health Initiative study found that women who took combination hormone therapy had a higher risk of breast cancer compared to those who took estrogen-only therapy. The risk of breast cancer was highest in women who took hormone therapy for more than five years. In addition, estrogen therapy has been linked to an increased risk of ovarian cancer, although the evidence is not as clear as for breast cancer.
Estrogen therapy can also increase the risk of blood clots, stroke, and cardiovascular events in some women. Estrogen therapy may not be appropriate for women with a history of breast cancer, ovarian cancer, blood clots, or stroke.
Hormone Replacement Therapy: A Treatment Option for Menopausal Symptoms in Women
Menopause is a natural biological process that occurs in women as they age, typically starting in their late 40s to early 50s. During menopause, the body gradually stops producing estrogen and progesterone, leading to symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and mood changes. These symptoms can be bothersome and impact a woman’s quality of life. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is a treatment option that involves the use of estrogen and/or progesterone to alleviate these symptoms. In this article, we will explore hormone replacement therapy, its benefits and risks, and how it can be used to manage menopausal symptoms in women.
Benefits of Hormone Replacement Therapy in Women
Hormone replacement therapy can alleviate several menopausal symptoms, including hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and mood changes. Hormone replacement therapy can also improve bone health and reduce the risk of fractures in postmenopausal women. In addition, hormone replacement therapy can improve cardiovascular health by reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Hormone Replacement Therapy and Vaginal Health: Managing Menopausal Symptoms
Menopause is a natural process that occurs in women as they age and marks the end of their reproductive years. During menopause, the body gradually stops producing estrogen and progesterone, leading to symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and mood changes. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is a treatment option that involves the use of estrogen and/or progesterone to alleviate these symptoms. This section will explore how hormone replacement therapy can improve vaginal health and manage menopausal symptoms.
Estrogen and Vaginal Health: Estrogen plays a critical role in vaginal health by maintaining the thickness, elasticity, and acidity of the vaginal walls. During menopause, the body’s natural estrogen levels decline, leading to several vaginal symptoms such as dryness, itching, and painful intercourse. These symptoms can be bothersome and impact a woman’s quality of life.
Hormone Replacement Therapy and Vaginal Health: Hormone replacement therapy can improve vaginal health and alleviate the symptoms of vaginal dryness, itching, and painful intercourse. Hormone replacement therapy can be administered in different forms, including vaginal creams, tablets, and rings. These forms of hormone replacement therapy deliver estrogen directly to the vaginal tissues, restoring their thickness, elasticity, and acidity.
Clinical studies have shown that vaginal estrogen therapy is effective in treating vaginal atrophy, a condition that occurs when the vaginal tissues become thin, dry, and inflamed due to low estrogen levels. Vaginal estrogen therapy can also improve urinary symptoms such as urgency, frequency, and incontinence.
Benefits of Hormone Therapy: Alleviating Menopausal Symptoms in Women
Hormone therapy is a treatment option that involves the use of estrogen and/or progesterone to supplement the body’s natural hormones during menopause. Menopause is a natural biological process that occurs in women as they age, typically starting in their late 40s to early 50s. During menopause, the body gradually stops producing estrogen and progesterone, leading to symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and mood changes. Hormone therapy can alleviate these symptoms and improve a woman’s quality of life. In this section, we will explore the benefits of hormone therapy for women.
Alleviating Menopausal Symptoms: Hormone therapy can alleviate several menopausal symptoms, including hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and mood changes. Clinical studies have shown that hormone therapy can reduce the frequency and severity of hot flashes and night sweats by up to 75%. Hormone therapy can also improve vaginal health and reduce the risk of urinary tract infections and painful intercourse. In addition, hormone therapy can improve bone health and reduce the risk of fractures in postmenopausal women.
Improving Cardiovascular Health: Hormone therapy can also improve cardiovascular health by reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke. Estrogen has a protective effect on the cardiovascular system, helping to maintain healthy blood vessels and reduce the risk of plaque buildup. Hormone therapy can also improve cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of blood clots.
Reducing the Risk of Colon Cancer: Hormone therapy has been shown to reduce the risk of colon cancer in women. Clinical studies have found that women who took hormone therapy had a lower risk of colon cancer than those who did not.
HRT isn’t just for women…
Symptoms of Hormone Imbalance in Men
Hormone imbalances in men can present many symptoms, ranging from physical to emotional. Some common physical symptoms of hormone imbalance in men include:
- hair loss
- fatigue
- decreased libido
- erectile dysfunction
Emotional symptoms can range from depression and anxiety to mood swings and irritability. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan. At Elite Health Online, our experienced doctors specialize in restoring hormonal balance with advanced hormone replacement therapy (HRT) methods. Get back on track with HRT.
Benefits of Hormone Replacement Therapy for Men
Improved muscle mass and bone density: Hormones are crucial in regulating bone and muscle health. As men age, testosterone levels decrease, leading to a loss of muscle mass and strength. Hormone Replacement Therapy can help increase muscle mass, improve strength, and enhance bone density, reducing the risk of fractures.
Increased energy and stamina: Hormone Replacement Therapy can help men restore their energy levels and stamina. Low hormone levels can cause fatigue and lack of energy, making it challenging to complete daily tasks. HRT can help boost energy levels, allowing men to participate in activities they enjoy.
Improved sexual function: Testosterone plays a critical role in sexual function in men. Low testosterone levels can lead to erectile dysfunction, low libido, and other sexual problems. HRT can help improve sexual function, leading to increased libido and better performance.
Better mood and mental clarity: Low hormone levels can lead to mood swings, irritability, and brain fog. HRT can help improve mood, reduce irritability, and enhance mental clarity, leading to a better quality of life.
Other potential benefits: Hormone Replacement Therapy can also help improve insulin sensitivity, reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, and improve overall health.
Types of Hormone Replacement Therapy for Men
There are several types of Hormone Replacement Therapy for Men, including injections, gels, patches, and pellets. Each type has advantages and disadvantages, depending on the individual’s needs.
Injections: Testosterone injections are administered in a healthcare setting and are usually given every two to four weeks.
The injections can lead to a rapid increase in testosterone levels, but the levels can drop significantly before the next injection.
Gels: Testosterone gels are applied topically to the skin and are absorbed into the body.
They are usually applied daily, and the testosterone levels remain stable throughout the day.
Patches: Testosterone patches are applied to the skin and are worn for 24 hours.
The patch can cause skin irritation in some men, and it can be challenging to keep it in place.
Pellets: Testosterone pellets are implanted under the skin for three to six months.
The pellets provide a steady release of testosterone, but the procedure can be costly.
Hormone Replacement Therapy for Men Treatment Process
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) is a treatment used to alleviate symptoms associated with low testosterone levels in men. HRT involves administering testosterone to the body through various methods.
How HRT is Administered:
HRT can be administered through injections, transdermal patches, gels, or pellets. Injections are typically given in the muscle every two to four weeks. Transdermal patches are placed on the skin daily and replaced every 24 hours. Gels are applied to the skin daily and absorbed into the bloodstream. Pellets are small implants placed under the skin every three to six months.
Treatment Schedule and Duration:
The treatment schedule and duration for HRT will vary depending on the individual’s needs and goals. Typically, the treatment lasts for several months to a few years. The dosage and frequency of the treatment will be adjusted as needed to maintain optimal hormone levels.
Monitoring Hormone Levels During Treatment:
It is important to monitor hormone levels during HRT to ensure the treatment works correctly and avoid potential complications. Hormone levels are typically monitored through blood tests taken at regular intervals. These tests will measure testosterone levels and other hormone levels to ensure that they remain within a healthy range.
Managing Side Effects of Hormone Therapy: Understanding the Risks and Benefits
Hormone therapy is a common treatment option for managing hormonal imbalances, menopause symptoms, and gender dysphoria. This therapy involves the use of natural or synthetic hormones administered through pills, patches, injections, or topical creams. While hormone therapy can be effective, it is associated with certain side effects that can impact a patient’s quality of life. In this section, we will explore the potential side effects of hormone therapy and how they can be managed.
Side Effects of Hormone Therapy: Hormone therapy has been linked to an increased risk of certain cancers, particularly breast and ovarian cancer. The Women’s Health Initiative study found that women who took combination hormone therapy had a higher risk of breast cancer compared to those who took estrogen-only therapy. The risk of breast cancer was highest in women who took hormone therapy for more than five years. In addition, hormone therapy has been linked to an increased risk of ovarian cancer, although the evidence is not as clear as for breast cancer.
Hormone therapy can also cause several other side effects, including:
- Hot flashes
- Vaginal dryness
- Mood changes
- Weight gain
- Headaches
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Insomnia
- Irregular bleeding
Managing Side Effects: To manage the side effects of hormone therapy, patients should discuss their symptoms with their healthcare provider. Depending on the severity of the symptoms, the healthcare provider may recommend changes to the dosage or form of hormone therapy. For example, switching from oral pills to transdermal patches may reduce the risk of blood clots and cardiovascular events.
Patients may also benefit from lifestyle changes such as exercise, a healthy diet, and stress management techniques to alleviate the symptoms of menopause and improve overall health. Alternative therapies such as acupuncture, meditation, and herbal supplements may also help manage symptoms, but patients should discuss these options with their healthcare provider before starting any new treatments.
Regular monitoring and follow-up are important for the early detection and management of any potential side effects or complications. Patients should attend regular check-ups and mammograms to monitor their breast health and overall health while on hormone therapy.
Hormone Therapy and Cancer Risks: Understanding the Clinical Guidelines
Hormone therapy is a common treatment for menopause symptoms and other hormonal imbalances. However, this therapy has been linked to an increased risk of certain cancers, including breast and ovarian cancer. In recent years, clinical guidelines have been developed to help healthcare providers and patients understand the risks and benefits of hormone therapy.
Hormone therapy involves using hormones, typically estrogen and progesterone, to alleviate the symptoms of menopause and other hormonal imbalances. Hormone therapy aims to supplement the body’s natural hormones and restore hormonal balance. Hormone therapy can be administered in different forms, including pills, patches, injections, and topical creams.
However, studies have shown that hormone therapy can increase the risk of certain cancers, particularly breast and ovarian cancer. The Women’s Health Initiative study found that women who took combination hormone therapy had a higher risk of breast cancer than those who took estrogen-only therapy. The risk of breast cancer was highest in women who took hormone therapy for more than five years. In addition, hormone therapy has been linked to an increased risk of ovarian cancer, although the evidence is not as clear as for breast cancer.
Cancer Risks:
While hormone therapy can be an effective treatment option for managing menopause symptoms and other hormonal imbalances, it is associated with an increased risk of certain cancers. Women who undergo hormone replacement therapy have a slightly higher risk of breast and ovarian cancer. According to the Women’s Health Initiative study, women who took combination hormone therapy had a higher risk of breast cancer than those who took estrogen-only therapy. The risk of breast cancer was highest in women who took hormone therapy for more than five years.
Clinical guidelines have been developed to help healthcare providers and patients make informed decisions about hormone therapy. The North American Menopause Society (NAMS) and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) have published guidelines on hormone therapy use. These guidelines recommend the appropriate use of hormone therapy, considering the patient’s risk factors and preferences.